PACCAR PX-9 Fuel System Diagrams That Won't Drive You Crazy
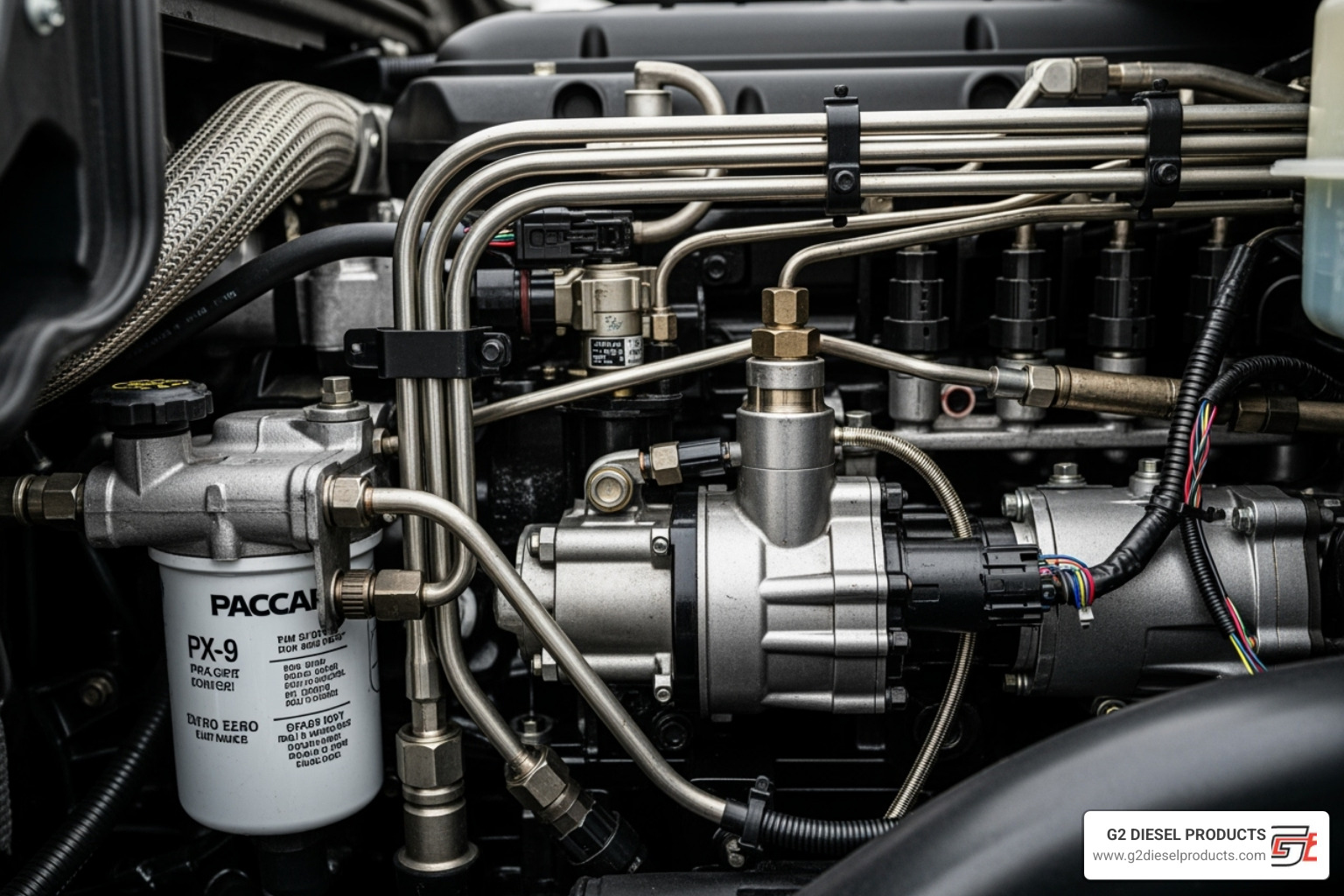
The paccar px-9 fuel system diagram pdf you're searching for is a roadmap to one of the most sophisticated diesel fuel systems on the road. Finding a clear, comprehensive diagram can be challenging, but understanding the system is key to effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Modern diesel engines like the PACCAR PX-9 use a High-Pressure Common Rail (HPCR) system operating at over 29,000 PSI. This isn't a simple mechanical system; it's a complex network of high-pressure components controlled by an advanced computer. Key features include an integrated fuel filtration module, precision fuel delivery controlled by the Electronic Control Module (ECM), and solenoid valve injectors with individual calibration codes.
This guide breaks down the PX-9 fuel system into understandable parts. You'll learn how fuel flows from the tank to the cylinder, the function of each component, and the maintenance required to keep your fleet running efficiently. Whether you're a technician troubleshooting a hard start or a fleet manager planning preventive maintenance, this information will save you time and money.
Deconstructing the Paccar PX-9 Fuel System: A Component-by-Component Guide
Think of the PACCAR PX-9 fuel system as a well-orchestrated symphony. Let's follow the fuel's journey from the tank to the combustion chamber to understand how each component contributes to the engine's performance.
From the Tank to the Pump: The Low-Pressure Circuit
The fuel's journey begins in the fuel tank. Suction lines draw diesel into the fuel filtration module, a critical component that cleans and prepares the fuel. Inside this module, a prefilter removes large debris, while a fine filter (typically 5 microns) catches smaller contaminants. A water separator uses centrifugal force to remove water, which is monitored by a water-in-fuel (WIF) sensor. For cold climates, a fuel heater prevents diesel from gelling. A hand priming pump is also included for bleeding air from the system after maintenance. Our guide on How to Prime a Paccar PX-9 Fuel System provides detailed instructions. Finally, the low-pressure gear pump (or lift pump) ensures a consistent flow of clean, warm fuel to the high-pressure circuit.
The High-Pressure Heart: Pump, Rail, and Injectors
Now the fuel enters the high-pressure circuit, where it's pressurized for injection. The High-Pressure Fuel Pump, driven by the engine, generates pressures exceeding 29,000 PSI. Modern PX-9 engines use a High-Pressure Common Rail (HPCR) system, not the older Cummins Accumulator Pump System (CAPS) found in some related engines.
The pressurized fuel is stored in the high-pressure common rail, a hydraulic accumulator that dampens pressure pulses and provides a steady supply to the injectors. A rail pressure sensor sends real-time data to the ECM, while a rail pressure release valve acts as a safety device and enables a limp-home function by maintaining minimum pressure if a fault occurs.
From the rail, high-pressure fuel lines deliver fuel to the solenoid valve injectors. These are sophisticated electronic devices that receive signals from the ECM to spray a precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber. Each injector has a unique injector calibration code that must be programmed into the ECM to ensure accurate fueling. Any unused fuel is returned to the tank via the return fuel circuit, completing the cycle.
At G2 Diesel Products, we manufacture reliable Diesel Engine Parts, including high-quality Products - Paccar Diesel Fuel Injectors, to keep your PX-9 running at its best.
The Brains of the Operation: How the ECM Controls the PX-9 Fuel System
The PACCAR PX-9's fuel system components are the musicians, but the Electronic Control Module (ECM) is the conductor. This sophisticated computer makes thousands of micro-adjustments every second to optimize performance, fuel economy, and emissions.
ECM and Sensor Integration
The ECM relies on a network of sensor inputs to make its decisions. Key data points include:
- Rail Pressure Sensor Data: Tells the ECM the exact pressure in the common rail, which is critical for calculating injection events.
- Engine Speed and Throttle Position: Inform the ECM of the engine's current state and the driver's power demand.
- Coolant Temperature: Allows the ECM to adjust fuel strategy for cold starts versus a fully warmed-up engine.
Based on these inputs, the ECM sends precise commands to actuator outputs, primarily the solenoid injectors and the high-pressure pump's controls. This creates a constant feedback loop for dynamic fuel delivery optimization.
Precision Control for Performance and Emissions
The ECM's precision is essential for meeting modern emissions standards. It manages several key parameters:
- Injector Timing: Controls when injection occurs in the combustion cycle to maximize power and minimize NOx emissions.
- Injection Duration (Pulse Width): Determines how much fuel is injected by controlling how long the injector stays open, measured in milliseconds.
- Rail Pressure Regulation: Continuously adjusts the high-pressure pump to maintain the target pressure in the common rail for optimal fuel atomization.
For diagnostics and maintenance, the DAVIE diagnostic tool allows technicians to communicate with the ECM. This is essential for tasks like reprogramming injector codes after a replacement. These codes are vital for optimizing fuel economy and meeting emissions standards, and skipping this step can lead to poor performance and fault codes.
Fueling for Success: PX-9 Fuel Requirements and Maintenance
Like a world-class athlete, your PACCAR PX-9 engine needs the right fuel and consistent maintenance to perform at its peak. Adhering to PACCAR's requirements is essential for reliability and longevity.
Choosing the Right Fuel for Your Paccar PX-9
Using the correct fuel protects your investment and ensures smooth operation. The PX-9 has specific requirements that are not optional.
PACCAR PX-9 Approved Fuel Types:
- Fuel Type: Ultra-Low-Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) with 15 ppm sulfur maximum is mandatory. Using other fuels can damage the aftertreatment system.
- Cetane Number: A minimum of 45 is required below 32°F (0°C), and 42 above. Higher cetane improves cold starts and smooths combustion.
- Fuel Lubricity: Fuel must meet ASTM D6079 or ISO 12156 standards to protect the high-pressure pump and injectors.
- Biodiesel Blends: Blends up to B20 (20% biodiesel) are approved if the biodiesel meets ASTM D6751 or EN 14214 and comes from a BQ-9000 accredited producer. Biodiesel may slightly reduce fuel economy and require shorter maintenance intervals.
For cold weather operation, use winterized diesel and quality anti-gel additives to prevent fuel from thickening and clogging filters.
Essential Fuel System Maintenance and Service Intervals
Consistent maintenance is the key to a long engine life. The PX-9's fuel system is sophisticated but manageable if you follow the schedule.
- Daily Checks: Visually inspect for fuel leaks and, most importantly, drain the water separator daily. This simple task prevents water from reaching and damaging high-pressure components.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: For standard operation, replace the fuel filter every 24,000 km (15,000 miles), 500 hours, or 6 months, whichever comes first. If using biodiesel blends (B6-B20), the interval changes to every 25,000 miles (40,000 km).
- Signs of a Clogged Filter: Look for reduced power, hard starting, or rough idle. Don't wait for these symptoms; stick to the schedule.
- Use OEM-Specification Filters: Aftermarket filters might not meet the specific flow and filtration requirements of the PX-9. Using filters that match original equipment specifications is crucial for protecting your engine and avoiding performance issues.
For more details, our resources on Paccar Fuel Systems and Truck Fuel Systems offer further insights.
Troubleshooting Common PX-9 Fuel System Problems
When your PACCAR PX-9 acts up, the fuel system is often the cause. Most problems follow predictable patterns, and understanding them can help you diagnose issues quickly.
Symptom: Low Power or Poor Acceleration
If your truck feels sluggish, your fuel system may be struggling. Common causes include:
- Clogged Fuel Filters: The most frequent culprit, restricting fuel flow to the engine.
- Air in Fuel Lines: Often occurs after maintenance if the system isn't primed correctly, causing inconsistent fuel delivery.
- Failing Low-Pressure Pump: The lift pump may not be supplying enough fuel to the high-pressure pump.
- Incorrect Rail Pressure: A faulty high-pressure pump or sensor can prevent injectors from spraying fuel effectively.
- Injector Malfunction: One or more failing injectors can create a power imbalance.
- Diagnostic Fault Codes: The ECM often logs codes that can point directly to the problem area.
Symptom: Hard Starting, No Start, or Rough Idle
Starting issues are a common sign of fuel system trouble. Check for:
- Loss of Prime: Air in the fuel lines prevents the engine from getting the fuel it needs to start.
- Low Fuel Pressure: Insufficient pressure in either the low or high-pressure circuits will prevent proper injection.
- Faulty Rail Pressure Sensor: If the sensor sends incorrect data to the ECM, fuel delivery will be miscalculated.
- Injector Issues: A sticking or failing injector can cause rough idling or prevent the engine from starting.
- Cold Weather Gelling: In cold temperatures, fuel can thicken and block filters if not properly treated with anti-gel additives.
Symptom: Excessive Smoke or High Fuel Consumption
If your truck is smoking or using too much fuel, investigate these possibilities:
- Leaking Injectors: An injector that drips fuel instead of spraying a fine mist leads to incomplete combustion and black smoke.
- Incorrect Injector Timing: If the ECM commands injection at the wrong time, fuel is wasted and emissions increase.
- High Return Fuel Flow: This indicates that fuel is bypassing the combustion process, often due to issues with the high-pressure pump or injectors.
For more troubleshooting insights, see our resource on Paccar MX Fuel System issues.
Where to Find a Paccar PX-9 Fuel System Diagram PDF and Service Manuals
Finding a single, perfect paccar px-9 fuel system diagram pdf can be difficult, but several reliable sources provide the technical information you need.
Official Paccar PX-9 Fuel System Diagram PDF Sources
Going straight to the manufacturer is always the best bet for accurate, up-to-date information.
- PACCAR Powertrain Website: A good source for operator manuals and service bulletins.
- Peterbilt and Kenworth Dealer Portals: These offer the most comprehensive service information, including detailed diagrams and procedures, but typically require a subscription for access.
- Subscription-Based Professional Services: Platforms that aggregate technical data are excellent resources for professional shops, though they come with a fee.
It's important to distinguish between an operator's manual (for drivers, with basic info) and a service manual (for technicians, with in-depth repair details). You can find official PACCAR PX-9 operator manuals here:
- [PDF] PX Operator Manual - PACCAR Powertrain
- [PDF] PX Operator Manual PACCAR PX-9 Engine (Y53-1185-1E1) - Peterbilt
Unofficial Manuals and What to Watch Out For
While the internet has many third-party resellers offering service manuals, you must be cautious. The biggest risk is outdated information. The PX-9 has evolved, and using a manual for the wrong model year can lead to incorrect repairs and costly damage. Always try to verify manual accuracy by cross-referencing part numbers and specifications with official sources when possible.
Understanding the System Without a Single Diagram
Component knowledge is more valuable than any single diagram. When you understand how each part works, you can mentally trace the fuel flow and diagnose problems logically. This guide is designed to be a conceptual diagram, explaining not just what is connected, but why it matters. Comparing the PX-9 with similar systems, like the one in our Paccar MX-11 Fuel System Diagram guide, can also deepen your understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions about the PX-9 Fuel System
Even with detailed technical information, some common questions about the PACCAR PX-9 fuel system persist. Here are answers to the ones we hear most often.
What is the correct fuel pressure for a Paccar PX-9?
The PX-9 has two distinct pressure circuits. The low-pressure circuit typically operates around 60-100 psi, ensuring a steady supply of fuel to the high-pressure pump. The high-pressure common rail (HPCR) is far more intense. At idle, rail pressure is between 2,900 to 8,700 psi (200 to 600 bar). Under load, it can climb significantly higher, reaching pressures needed to atomize fuel into a fine mist for efficient combustion.
How often should I change the fuel filters on a PX-9?
For standard service, PACCAR recommends changing the fuel filter every 24,000 km (15,000 miles), 500 hours, or 6 months, whichever comes first. If you use biodiesel blends (B6-B20), the interval is more frequent at every 25,000 miles (40,000 km) because biodiesel can clean deposits from the tank, clogging the filter faster. Always consult your specific PACCAR PX-9 operator's manual, as your duty cycle may require a different schedule.
What is the Cummins Accumulator Pump System (CAPS) and does the PX-9 use it?
This is a common point of confusion due to the engine's history. The PACCAR PX-9 is based on the Cummins ISC/ISL engine family, some of which used the Cummins Accumulator Pump System (CAPS). However, modern PACCAR PX-9 engines use a High-Pressure Common Rail (HPCR) system, not CAPS. The HPCR system offers superior control, efficiency, and emissions performance. While the PX-9 shares heritage with Cummins, it runs on a more contemporary fuel system design.
Conclusion
Mastering Your Paccar PX-9 Fuel System
Your search for a paccar px-9 fuel system diagram pdf is just the start. True mastery comes from understanding how the system's components work together. You now have the foundational knowledge to diagnose issues systematically, from low power to hard starts.
You've learned about the complexity of the High-Pressure Common Rail system and the critical roles of the filtration module, high-pressure pump, common rail, and precision injectors. This knowledge, combined with a commitment to proper maintenance and the use of high-quality fuel, is your best defense against costly downtime.
This understanding empowers you to make informed decisions for your fleet, whether you're training technicians or planning maintenance schedules.
At G2 Diesel Products, our expertise in manufacturing high-quality diesel fuel injectors comes from a deep understanding of what engines like the PX-9 need to perform. When you need replacement parts, you need components that match the precision of the original system.
For reliable, high-performance replacement injectors that keep your PX-9 running strong, explore our catalog at https://www.g2dieselproducts.com/shop-volvo-mack-kenworth-paccar-diesel-fuel-injectors. We're here to help keep your trucks on the road and making you money.
