PACCAR MX13 Fuel System Diagrams That Actually Make Sense
Why Understanding Your PACCAR MX13 Fuel System Diagram Matters
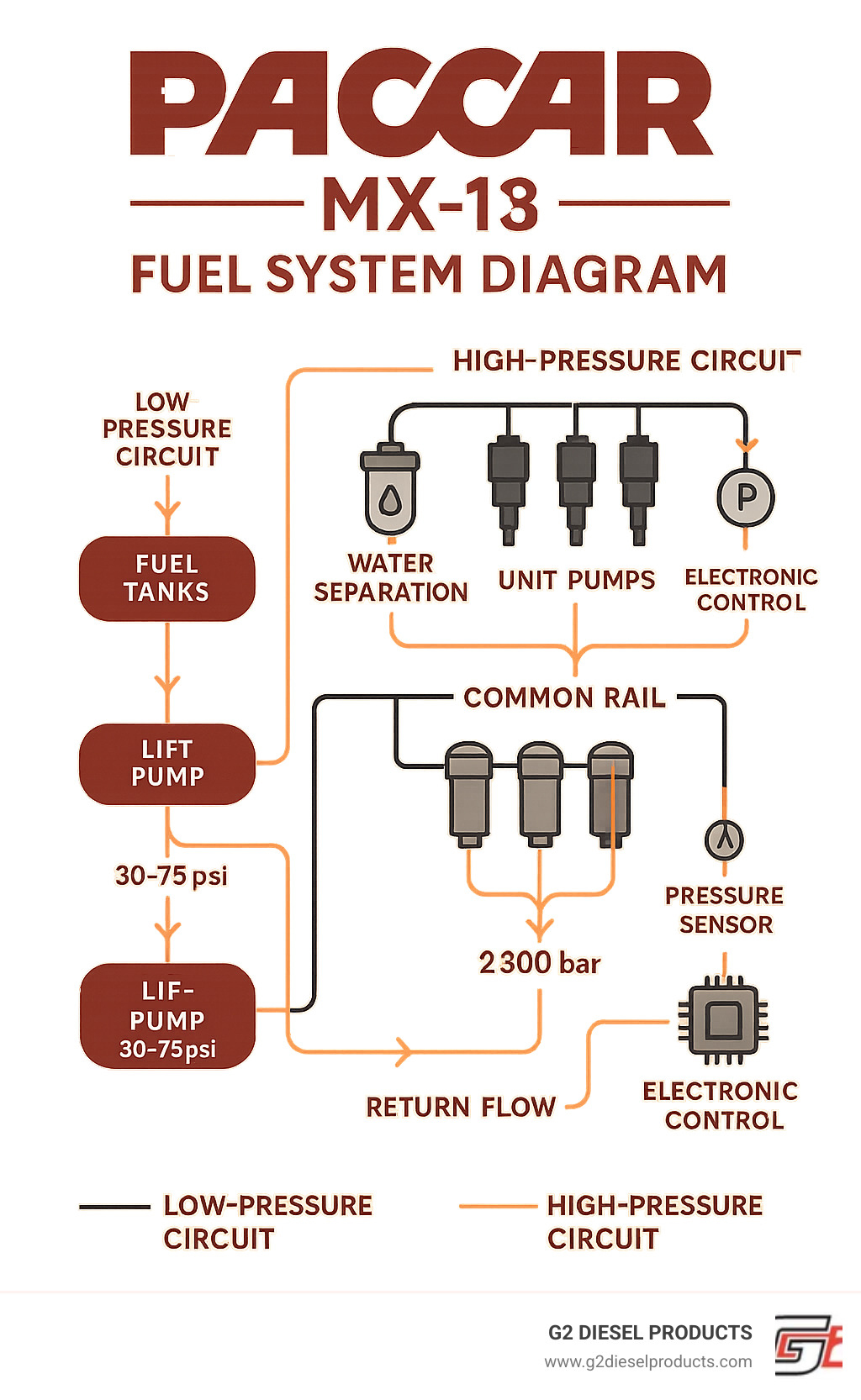
A PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram maps the path of diesel fuel from the tank to the injectors, flowing through a high-pressure common rail system that reaches up to 2,500 bar (36,260 psi).
Key components you'll find in every PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram:
- Low-pressure circuit: Fuel tanks → chassis pre-filter → lift pump (30-75 psi) → fuel filtration module
- High-pressure circuit: Unit pumps → common rail → solenoid valve injectors → return lines
- Management systems: Water-in-fuel detection, pressure sensors, electronic controls
- Filtration: Two-stage system (30 micron primary, 4-5 micron secondary)
As one veteran diesel technician puts it: "I've never seen a $5,000 high-pressure pump failure that couldn't have been prevented by a 30-second water drain."
When your MX-13 experiences hard starts, rough idling, or low fuel pressure codes like P0087, this diagram is your roadmap for systematic troubleshooting. It allows you to trace the fuel flow and pinpoint the exact source of the problem, saving you from guesswork and unnecessary part replacements.
The MX-13's common rail design allows for multiple injection events per combustion cycle, creating cleaner burns and better fuel economy than older mechanical systems. This sophistication makes understanding the system vital for proper maintenance and diagnosis.
Understanding the PACCAR MX-13 High-Pressure Common Rail System
The PACCAR MX-13 engine, found in modern Kenworth and Peterbilt trucks, owes its reliability and efficiency to its advanced high-pressure common rail system. This technology is a significant leap from older, less efficient mechanical injection systems. The system boosts performance by maintaining fuel pressure up to 2,500 bar (36,260 psi). This extreme pressure creates superior fuel atomization—misting fuel into the combustion chamber for a more complete and efficient burn.
This modern system also enables multiple injection events within each combustion cycle. Instead of a single blast of fuel, the system delivers several precise, small injections. This results in a cleaner burn, lower emissions, better fuel economy, and noticeably quieter and smoother engine operation. You can learn more about the MX-13 engine's capabilities on PACCAR's official page.
How Common Rail Technology Boosts Performance
The common rail system maintains constant, immense pressure, ready for immediate injection. This allows for perfectly timed injection events that optimize performance and efficiency:
- Pilot Injection: A small amount of fuel is injected before the main event to initiate smooth combustion, reducing engine noise.
- Main Injection: The primary fuel charge is delivered to generate power.
- Post-Injection: Additional small injections may occur after the main one to control emissions, manage exhaust temperatures, and assist with Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) regeneration.
This precise control over fuel injection leads directly to a cleaner burn, which translates to improved fuel economy and reduced emissions. It's a key feature of the PACCAR MX fuel system, which you can read more about on our dedicated page.
The Brains Behind the Brawn: Electronic Controls
The genius behind the MX-13's performance is its electronic control system, led by the Engine Control Module (ECM). The ECM acts as the brain, processing real-time data from a network of sensor inputs that monitor fuel pressure, temperature, engine speed, and load.
Based on this data, the ECM precisely dictates:
- Precise fuel timing and duration for each injector.
- The exact amount of fuel needed for optimal power and efficiency.
- The required injection pressure for perfect atomization.
This sophisticated electronic control ensures optimal combustion under all operating conditions, from cold starts to heavy hauling. It is also vital for emissions management, helping the truck meet strict environmental regulations. The seamless system integration of these controls is what makes the PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram an essential blueprint for understanding your engine's peak performance.
Decoding the PACCAR MX13 Fuel System Diagram: Key Components and Fuel Flow
To understand how the MX-13 engine is fueled, we can trace its path on the PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram. This map details the fuel's journey through two primary circuits: low-pressure and high-pressure, plus a return flow to the tank.
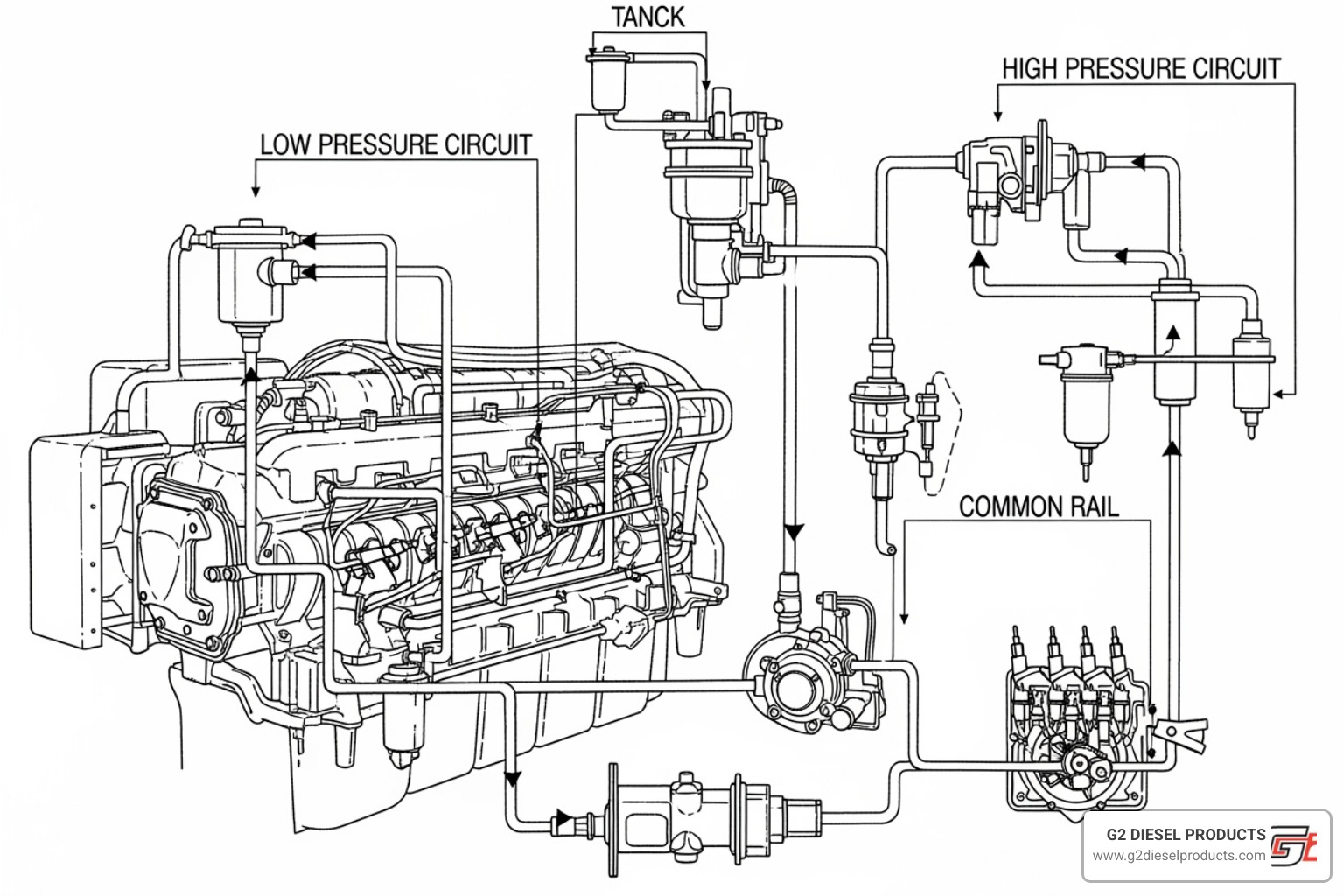
The Low-Pressure Circuit: From Tank to Pump
The fuel's journey begins in the fuel tanks. It is then drawn through the chassis pre-filter, which removes large particles (over 30 microns) and separates water. A Water-in-Fuel (WIF) sensor in this unit warns the driver if water accumulates.
Next, the fuel lift pump (typically a gear pump) creates an initial pressure of 30-75 psi, ensuring a steady flow to the engine's main fuel filtration module. This module often contains a hand priming pump for purging air from the system and may include a fuel heater to prevent gelling in cold weather.
Before entering the high-pressure circuit, the fuel passes through a secondary, finer filter (4-5 microns). This two-stage filtration is critical for protecting the precision components that follow.
The High-Pressure Circuit: Powering the Injectors
Clean fuel now enters the high-pressure pump. The MX-13 uses a block-integrated design that reduces external lines, improving reliability. This pump generates pressures up to 2,500 bar (36,260 psi) to atomize the fuel for efficient combustion.
From the pump, the high-pressure fuel enters the common rail, a fortified reservoir that distributes fuel to all injectors. The rail is equipped with a fuel pressure sensor and a fuel temperature sensor that send critical data to the ECM. A pressure relief valve provides over-pressure protection.
Finally, the solenoid valve injectors receive the high-pressure fuel. Controlled electronically by the ECM, they spray a fine mist of fuel into each cylinder with precise timing. Any unused fuel, along with fuel used for cooling the injectors, is sent back to the tank via injector return lines. G2 Diesel Products offers high-quality injectors designed for the PACCAR MX-13, and you can explore our Smart F2P Injectors and other options.
Essential Maintenance for a Healthy MX-13 Fuel System
Your PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram shows a complex system, but its health depends on a simple principle: clean fuel and regular maintenance save you from costly repairs. The high-pressure components are unforgiving of contamination and neglect.

Daily checks, especially draining the water separator, are essential. Water is a primary cause of damage to injection pumps and injectors. Make this 30-second check part of your pre-trip inspection.
Fuel filter service intervals are based on your truck's usage:
- Standard Duty (Highway): Change every 75,000 miles or 12 months.
- Severe Duty (Construction, Logging): Change every 30,000 miles or 6 months.
- B20 Biodiesel Blends: Change every 25,000 miles, as biodiesel can loosen deposits that clog filters.
Step-by-Step Fuel Filter and Water Separator Service
Changing fuel filters correctly is crucial to avoid air intrusion or leaks.
Before you begin: Ensure the engine is cool and work in a well-ventilated area. If applicable, close the manual fuel shut-off valves.
Required Tools: Clean drain container, fuel filter bowl wrench, 32mm hexagonal socket, torque wrench, clean diesel fuel, and clean rags.
- Drain Water: Place a container under the separator and drain any accumulated water.
- Remove Filters: Use your filter wrench to remove the old filters. Expect some fuel spillage.
- Clean Housing: Thoroughly clean the filter housing, ensuring no debris falls inside.
- Lubricate Seals: Apply a light coat of clean diesel fuel to all O-rings and seals on the new filters.
- Install Filters: Hand-tighten the new filters, then use a torque wrench to tighten to the specified 30 lb-ft. Do not over-tighten.
- Prime System: Use the hand priming pump for 150 seconds to fill the filters and purge air. You should feel resistance build. Wait 60 seconds, then pump for 25 more strokes.
- Check for Leaks: Start the engine and let it idle for 5 minutes, carefully checking all connections for leaks.
For the complete official procedure, refer to PACCAR's fuel filter maintenance bulletin.
Fuel Quality and Cold Weather Operations
Your MX-13 requires high-quality fuel for performance and warranty coverage. Always use Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) meeting ASTM D975 standards.
- Cetane Number: Use a minimum of 45 cetane below 32°F and 42 cetane in warmer temperatures.
- Fuel Lubricity: Use fuel with a wear scar diameter of 0.02 inches or less to protect high-pressure components.
- Biodiesel: Blends up to B20 are approved if they meet ASTM D6751 and come from a BQ-9000 Accredited Producer.
In cold weather, use winter-blend fuel to prevent gelling. Keep tanks full to minimize condensation and use your truck's fuel heater. Only use anti-gel additives that are approved by PACCAR to avoid damaging the emissions system.
When it's time for replacement parts, G2 Diesel Products offers high-quality PACCAR diesel fuel injectors that meet your engine's demanding specifications.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with an MX-13 Fuel System Diagram
When your MX-13 experiences issues like low power, rough running, or a no-start condition, your PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram is the best tool for diagnosis. It allows for a systematic approach to pinpoint the problem's source, rather than guessing with random part replacements.

Diagnosing Air Intrusion and Low Pressure using a PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram
Air intrusion is a common cause of fuel system problems, disrupting the steady flow of diesel required for proper engine function. Symptoms often include:
- Hard starting or a complete no-start condition.
- Engine losing its prime after sitting.
- Rough idling or an intermittent rough run.
- Engine stalling or shutting down under load.
- Visible air bubbles in clear fuel lines or a sight glass.
Air can enter the system through loose or cracked fuel lines (especially on the suction side), damaged O-rings on filters or fittings, or a faulty water separator. To diagnose low pressure, a technician can use a gauge to check pressure at various points in the system. Diagnostic codes like P0087 (Fuel Rail Pressure Too Low) also point to this issue. Low readings could indicate a clogged filter, a restricted line, or a failing lift pump. For more examples, forums like The Truckers Report can offer insight.
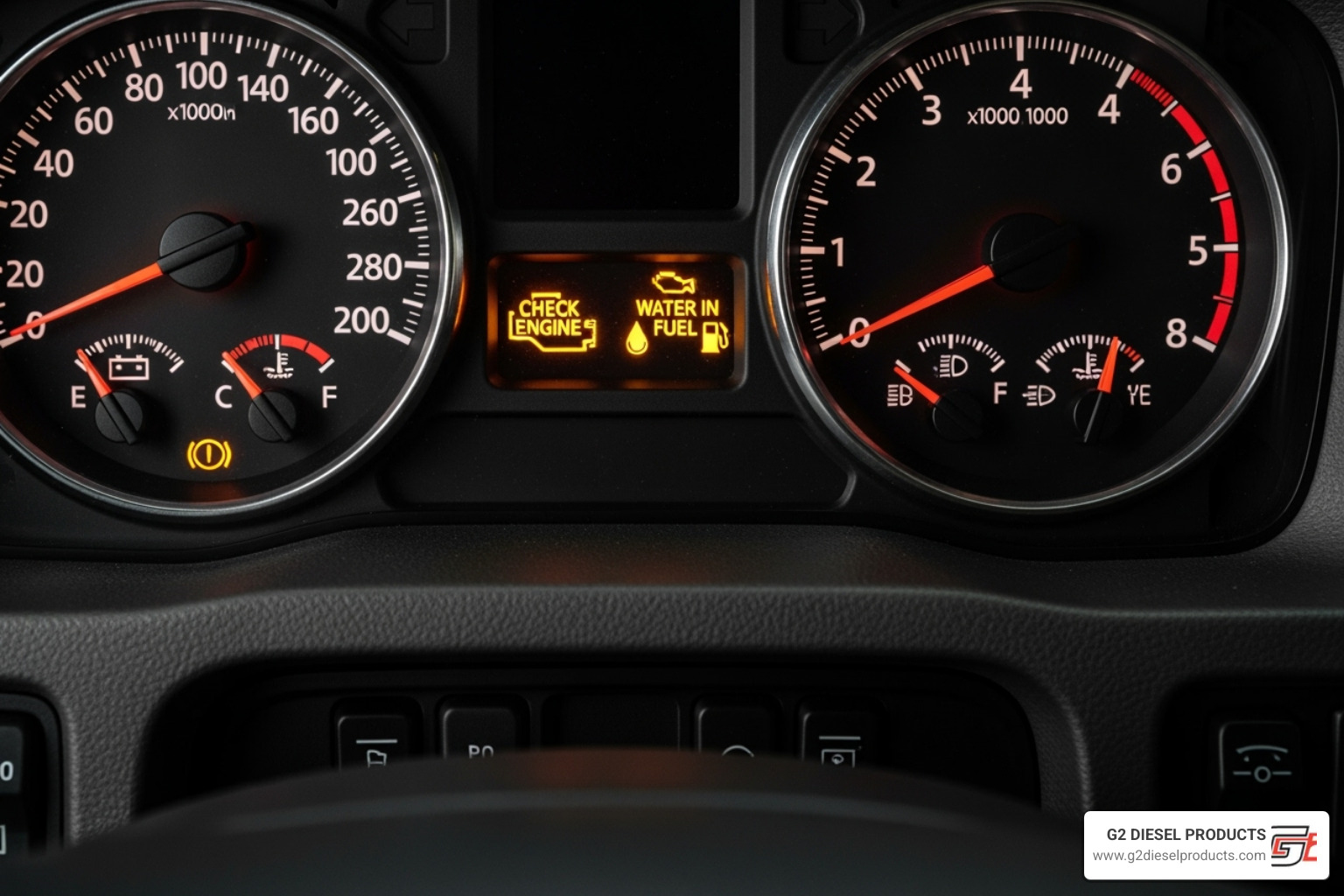
Understanding Dashboard Warning Lights related to the PACCAR MX13 fuel system
Your dashboard lights are critical indicators. Never ignore them.
Water-in-Fuel (WIF) Light: Indicates water in the fuel separator. Action: Pull over safely and drain the separator immediately. If the light persists after draining, the sensor may be faulty or there's a significant water contamination issue. Ignoring this can lead to costly high-pressure system damage.
Check Engine Light (CEL): A general warning that the ECM has detected a fault. Action: If the light is solid, have the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) read as soon as possible to identify the specific problem.
Stop Engine Light: Signals a critical problem that could cause major engine damage. Action: Safely pull over and shut down the engine immediately. Do not restart until a qualified technician has diagnosed the issue.
Low Fuel Pressure Warning: May appear as a dedicated light or a CEL code like P0087. Action: Investigate immediately. Check fuel levels, then look for clogged filters or fuel line restrictions.
DPF Regeneration Lights: A functioning fuel system is required for proper DPF regeneration. If you have recurring DPF issues, an underlying fuel system problem could be the cause. Action: Follow all DPF regeneration procedures. If problems persist, have the fuel system inspected.
Frequently Asked Questions about the PACCAR MX-13 Fuel System
Here are concise answers to the most common questions we receive about the MX-13 fuel system and its PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram.
How often should I drain the water from the fuel separator?
Ideally, you should drain the water separator daily as part of your pre-trip inspection. Water is heavier than diesel and settles in the filter bowl, posing a significant risk to the high-pressure pump and injectors. Daily draining is the best preventative measure, especially in humid climates, and takes less than a minute. Do not wait for the WIF light to come on.
What happens if I get air in the fuel system?
Air in the fuel system disrupts the pressurized flow of diesel, leading to symptoms like hard starting or no-start conditions, rough idling, engine misfires, and unexpected stalling. The engine may also "lose its prime" after being shut off. If priming the system doesn't resolve the issue, you must inspect all fuel lines, seals, and fittings on the suction side for leaks, as even a tiny crack can introduce air.
Can I use any diesel fuel in my MX-13 engine?
No, the MX-13 requires specific fuel to operate correctly and maintain its warranty. Always use Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) that meets ASTM D975 standards. Pay attention to the cetane rating (minimum 42, 45 in cold weather) and ensure good lubricity. Approved biodiesel blends up to B20 are acceptable if they meet ASTM D6751 standards, but they require more frequent filter changes. Never use gasoline, alcohol, or unapproved additives.
When it comes time to replace fuel system components, G2 Diesel Products has you covered with high-quality PACCAR diesel fuel injectors designed to work perfectly with quality fuel in your MX-13 system.
Conclusion: Keeping Your MX-13 Running Strong
Your PACCAR MX13 fuel system diagram is an essential tool, providing the blueprint to understand and maintain one of the most sophisticated diesel engines on the road. Understanding this system empowers you to perform proactive maintenance and effective troubleshooting, preventing minor issues from becoming costly failures.
The key to longevity is diligence. That daily 30-second water drain, adherence to filter service intervals, and use of high-quality fuel are your best insurance policies. These practices protect the precision components that operate under immense pressure, ensuring your engine runs reliably for hundreds of thousands of miles.
When replacement time does come, especially for critical components like fuel injectors, choosing parts that match your engine's precision is paramount. At G2 Diesel Products, our team in Harrisburg, PA, specializes in manufacturing high-quality diesel fuel injectors that meet the rigorous standards your MX-13 requires. We focus on innovation and reliability to ensure our injectors deliver the precise fuel metering your common rail system demands.
Your MX-13 is built for the long haul. Take care of its fuel system with quality maintenance and quality parts, and it will take care of you.
Ready to keep your fuel system at peak performance? You can shop for high-quality PACCAR diesel fuel injectors directly on our website.
