The Diesel Dilemma: Common Injector Problems and How to Diagnose Them
The Diesel Dilemma: Understanding Fuel Injector Problems
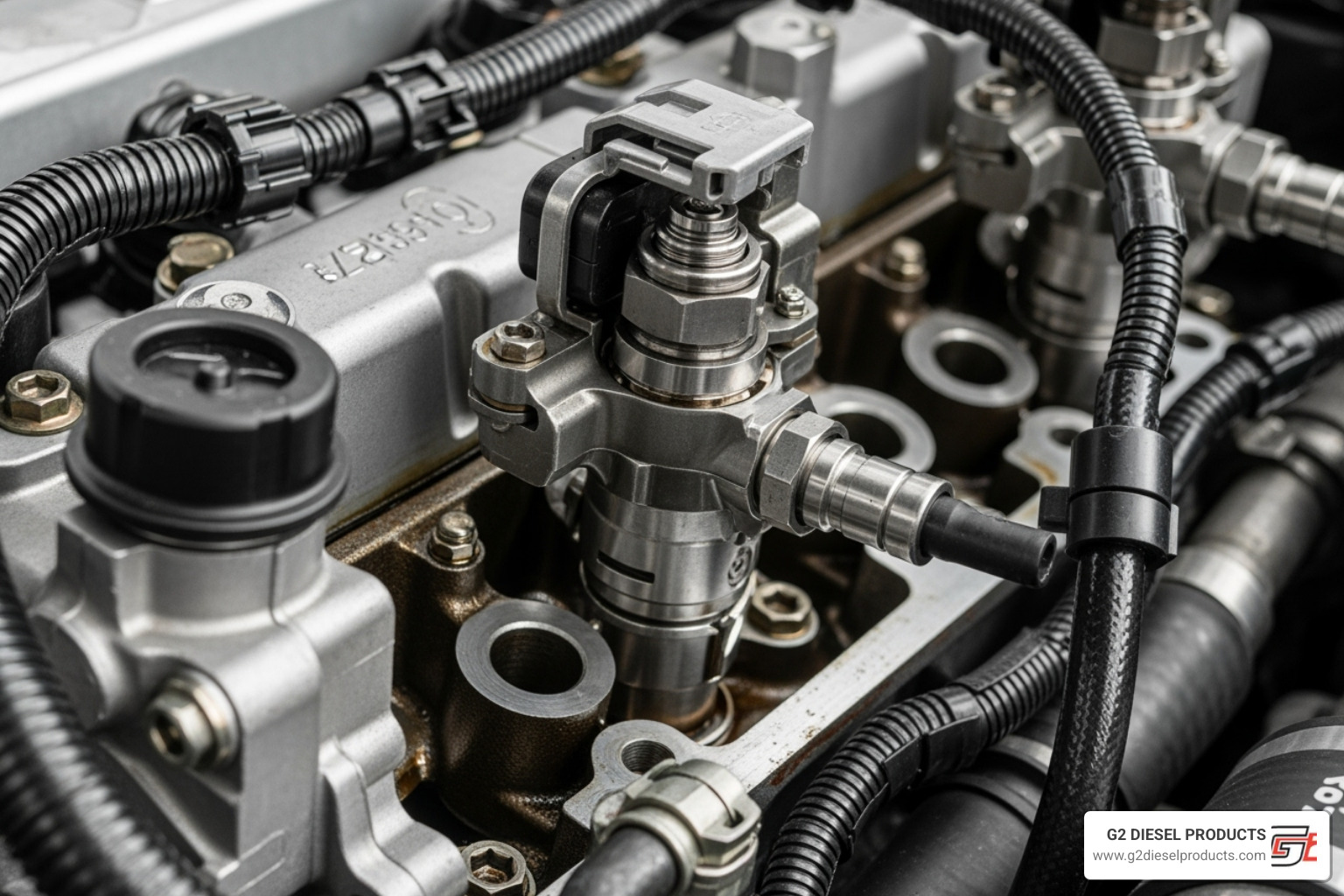
Title: Diesel Fuel Injector System Alt Text: Close-up of a modern common rail diesel fuel injector installed in an engine.
If your diesel engine is struggling with issues like rough idling, misfires, poor fuel economy, or power loss, you might be facing fuel injector problems diesel owners often encounter. Other common signs include difficulty starting, excessive exhaust smoke (black, white, or blue), and a distinct fuel smell. Spotting these signs early can save you from costly repairs and downtime.
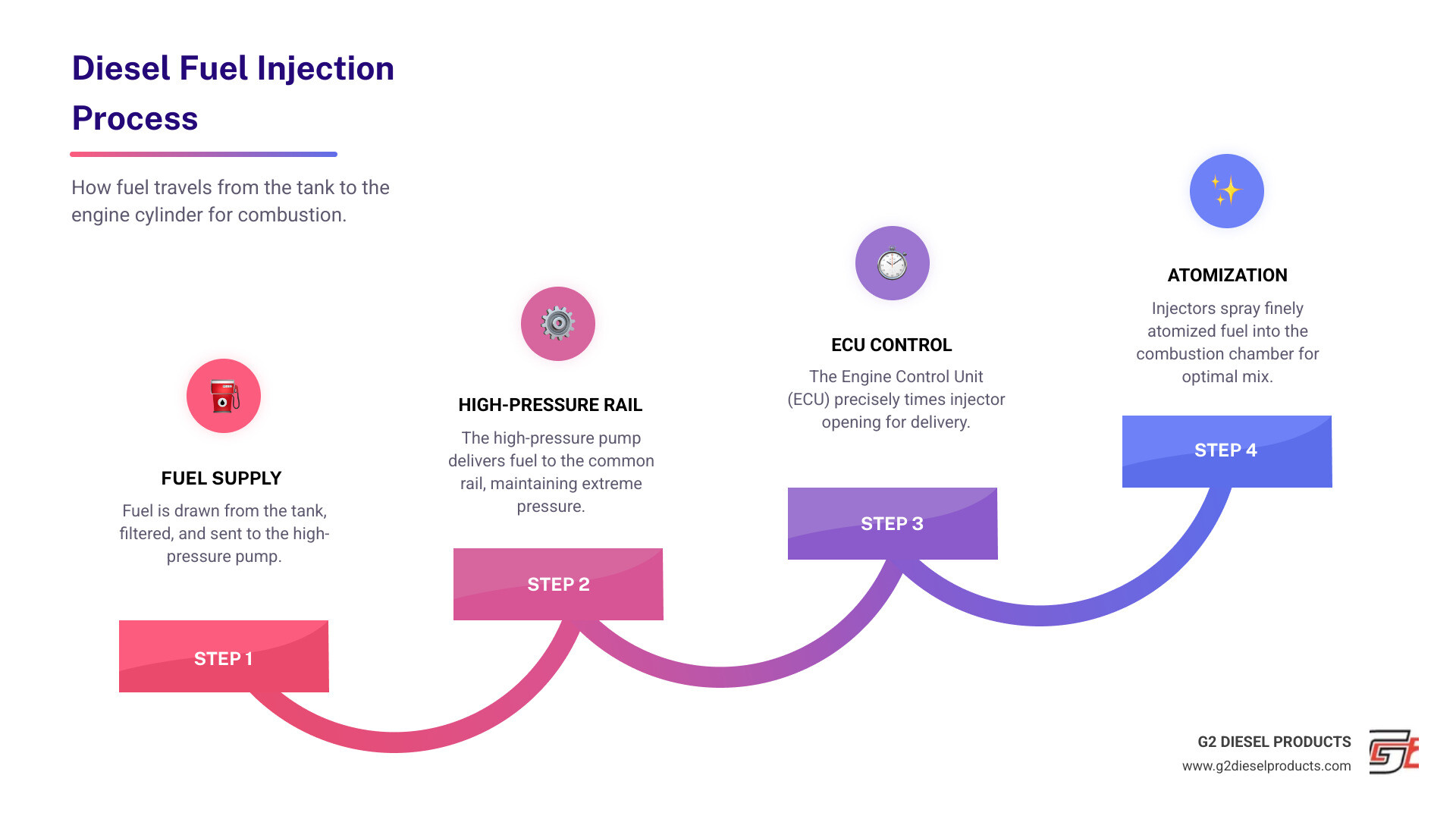
At the heart of a diesel's power are its fuel injectors, which deliver a precise, high-pressure spray of fuel into the engine's cylinders. When injectors fail, engine performance suffers. Modern common rail systems, while powerful, place immense stress on injectors, as they can fire multiple times per engine cycle. This constant work leads to wear and tear, making it crucial to understand these components to keep your fleet running smoothly.
Spotting the Trouble: 7 Common Symptoms of Failing Diesel Injectors
When your diesel engine's fuel injectors start to fail, they provide clear warning signs. Learning to recognize these symptoms of fuel injector problems diesel engines develop can help you address issues early, saving you from major headaches and expensive repairs down the road.
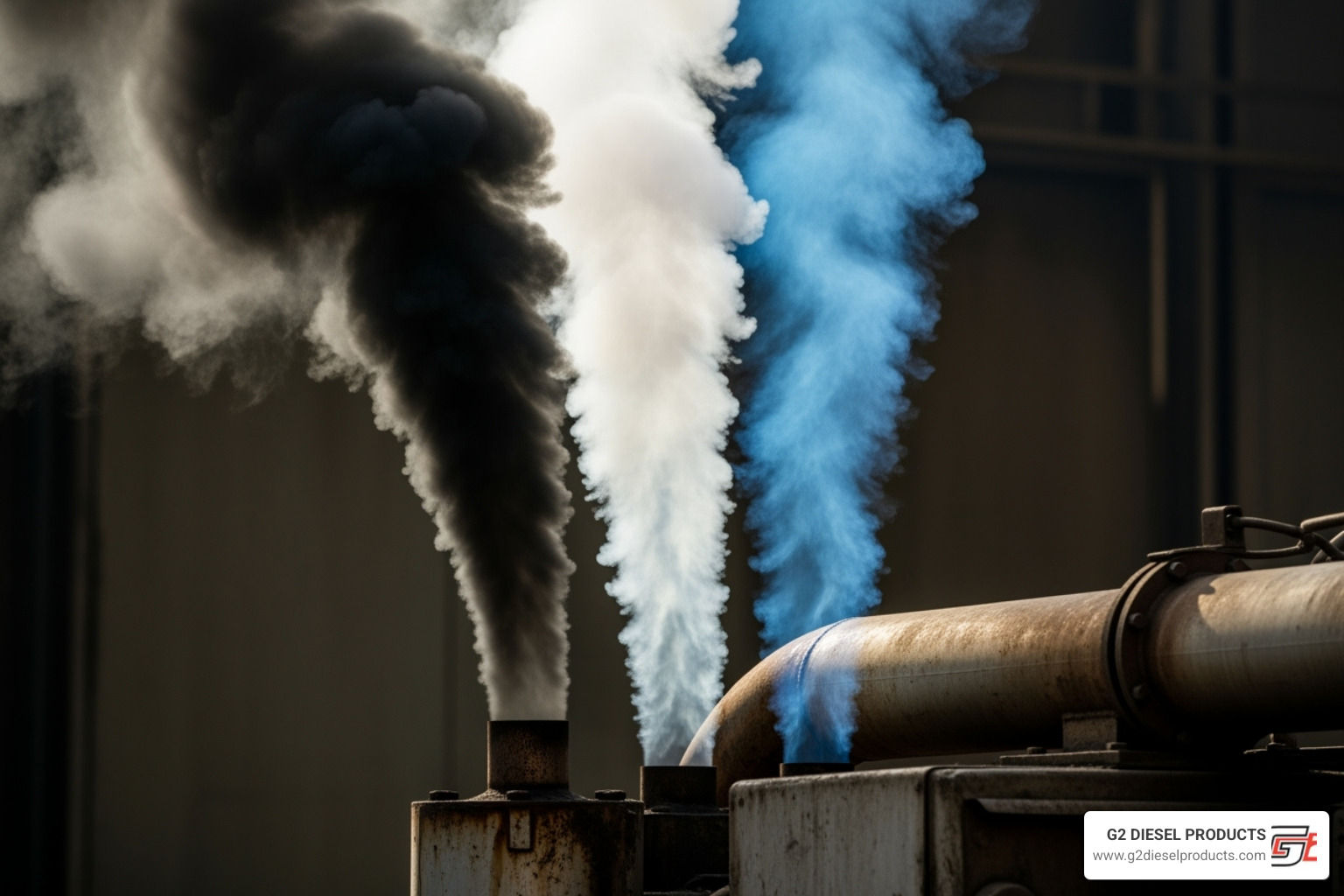

Title: Diesel Exhaust Smoke Colors Alt Text: Comparison of black, white, and blue exhaust smoke from a diesel engine, indicating different problems.
Common Symptoms of Fuel Injector Problems: Diesel Engine Warning Signs
- Rough Idling: An imbalanced fuel delivery causes the engine to shake and run unevenly at rest.
- Engine Misfires: An injector failing to deliver the correct amount of fuel at the right time causes the engine to stumble or hesitate.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A noticeable drop in fuel efficiency is a key sign. Faulty injectors don't atomize fuel properly, leading to a rich or lean mixture that wastes fuel.
- Loss of Power: The truck may feel sluggish, struggle on hills, or accelerate slowly because the engine isn't receiving the fuel it needs to produce its designed power.
- Difficulty Starting: If your engine cranks longer than usual or fails to start, especially when cold, the fuel delivery system is a likely suspect.
- Excessive Exhaust Smoke: The color of the smoke tells a story. Black smoke indicates too much fuel. White smoke suggests unburned fuel passing through the exhaust. Blue smoke typically means oil is being burned, which can happen if bad injectors wash oil from cylinder walls.
- Fuel Smell: A raw diesel odor often means an injector is leaking externally or has a bad seal, creating a safety hazard and wasting fuel.
For more details, see our guide on the signs of an injector going bad.
The Check Engine Light and What It Means
The check engine light is your engine's primary warning signal. Modern diesel engines use sensors to detect fuel delivery problems, and the Engine Control Unit (ECU) will log a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) when an issue arises.
Common codes like P0087 Low Fuel Rail Pressure, or others related to misfires and injector circuits, provide a starting point for diagnosis. A professional scan is crucial to interpret these codes correctly and identify the root cause. Don't ignore the check engine light; it's your first alert that a problem needs attention.
Understanding the Main Causes of Fuel Injector Problems in Diesel Engines
Diesel injectors operate under extreme conditions, making them susceptible to issues that cause the fuel injector problems diesel owners frequently encounter. Failures typically arise from two main sources: fuel quality issues and mechanical wear. Understanding these causes is the first step toward prevention.
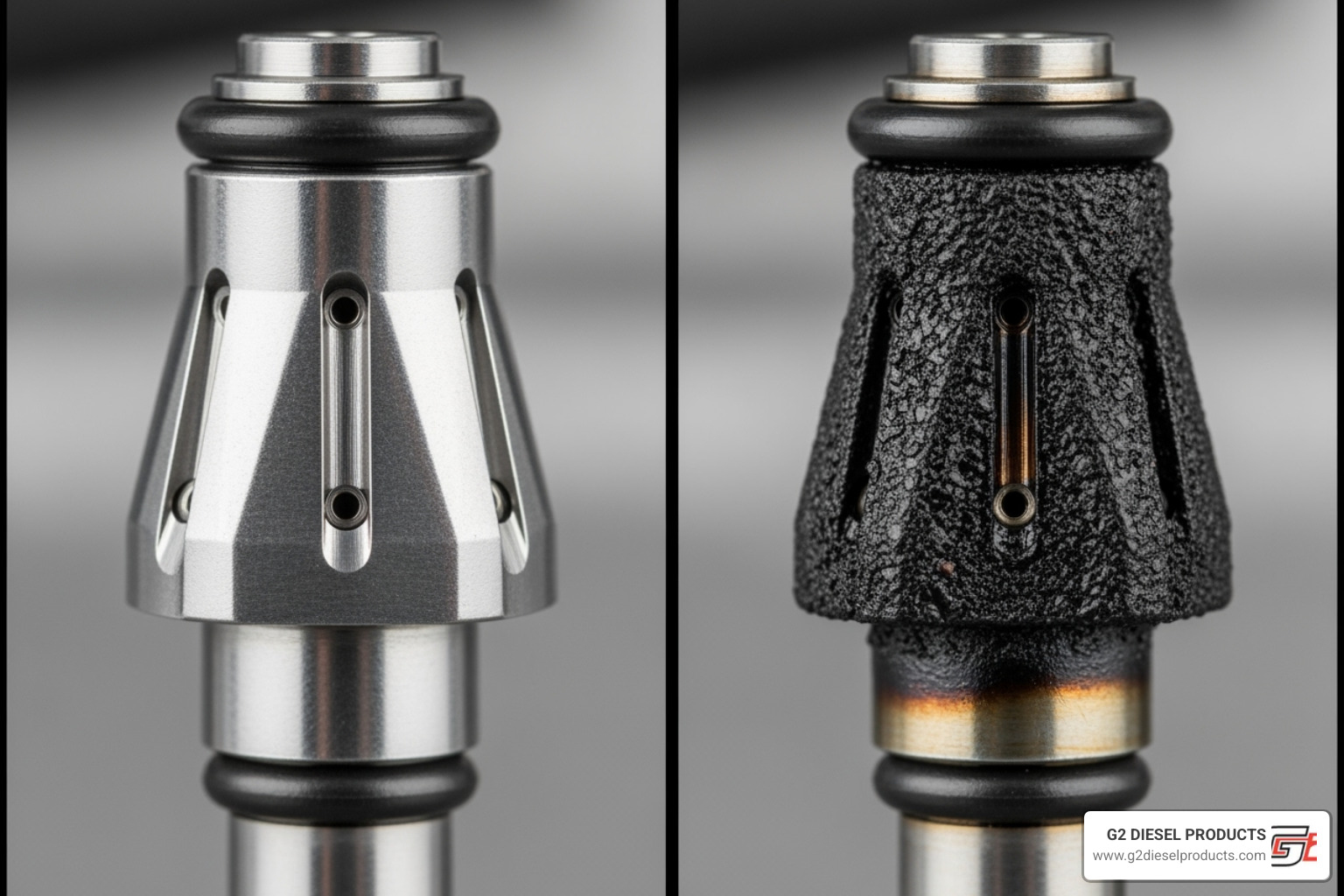

Title: Clean vs. Clogged Diesel Injector Alt Text: A side-by-side comparison of a clean diesel fuel injector nozzle and one clogged with carbon deposits.
Fuel Quality and Contamination
The fuel running through your injectors is their lifeblood; if it's contaminated, it can cause serious damage.
- Low-Quality Fuel: Diesel with impurities or poor lubrication can cause premature wear and deposit buildup inside the injector.
- Water Contamination: Water is a primary enemy, causing corrosion on precise internal components. It also promotes microbial growth (the 'diesel bug'), which clogs filters and injectors.
- Debris and Rust: Tiny particles of dirt or rust can enter the fuel system and abrade delicate injector surfaces. The tolerances in modern common-rail systems are incredibly tight (1-3 microns), so even the smallest speck can cause significant damage.
- Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) Lubricity: While better for emissions, the process to create ULSD reduces its natural lubricity. If the additives used to compensate are insufficient, it can lead to increased wear on injector components.
Learning how to prevent diesel fuel contamination is a key preventative measure.
Mechanical Wear and Internal Failures
The intense demands of modern engines can lead to mechanical breakdowns.
- High Mileage Wear: Like any mechanical part, injectors wear out over time. After 100,000 miles, an inspection is recommended. Today's common-rail injectors operate at over 23,000 psi and fire multiple times per cycle, leading to significant wear.
- Internal Deposits (IDID): Deposits can form on internal parts like injector needles, especially in High-Pressure Common-Rail (HPCR) systems. This can cause injectors to stick, leading to incorrect fuel delivery or high internal leakage. This can sometimes cause a change in engine sound, which is why it's good to understand diesel injector noise reduction.
- Other Mechanical Failures: Issues like ball seat erosion (causing leaks) and a stuck needle valve (stopping fuel flow) are common.
- Incorrect Installation: Simple mistakes like missing sealing rings or improper torque can cause leaks, poor performance, and even engine damage. The symptoms of bad injector seating can be immediate and severe.
These factors highlight why precision and quality are critical for diesel fuel injectors.
From Suspicion to Certainty: How to Diagnose Injector Issues
When your diesel truck shows signs of trouble, a systematic approach to diagnosis is essential to avoid replacing the wrong parts. While some checks are simple, pinpointing the exact cause of fuel injector problems diesel engines have often requires professional tools and expertise.
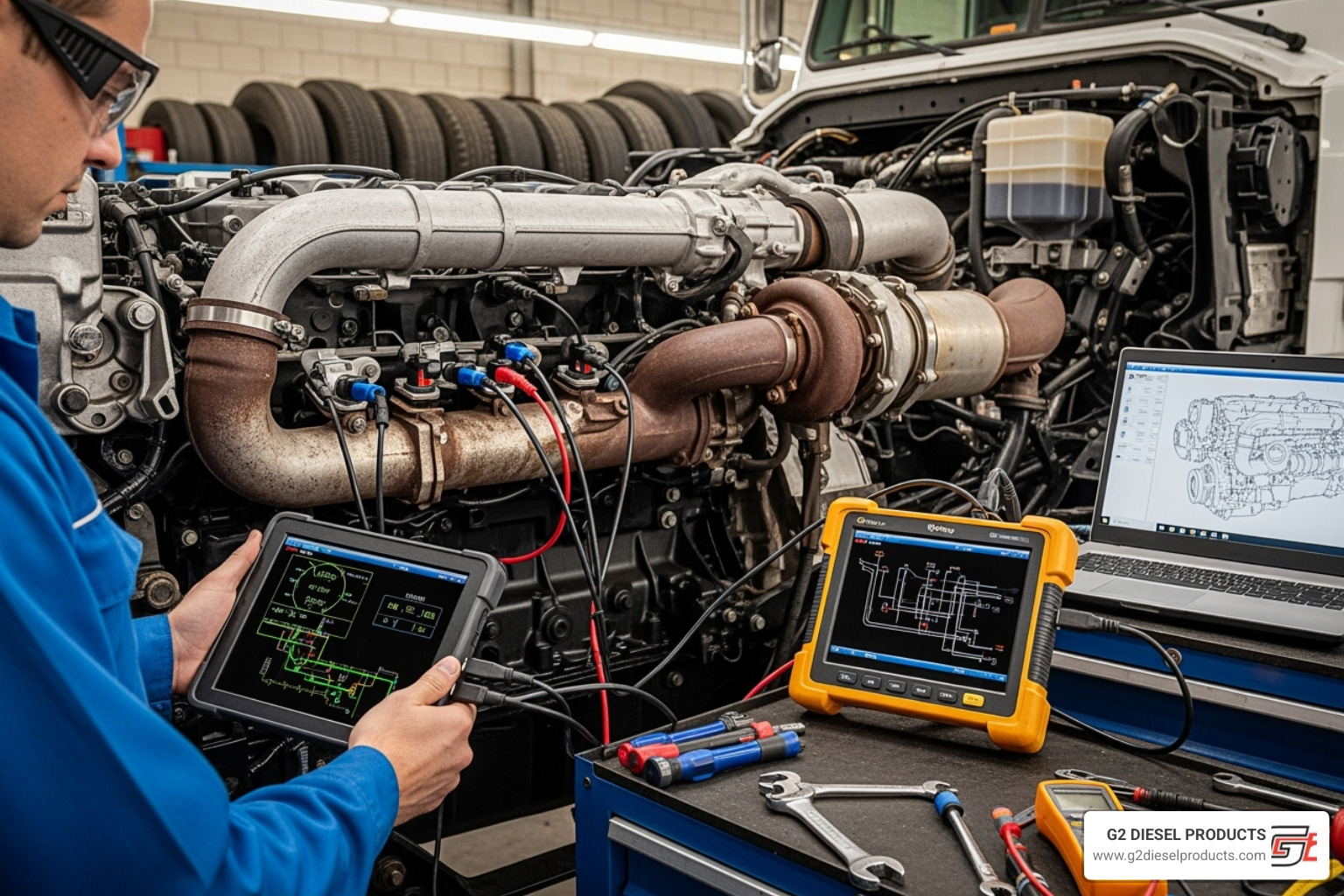

Title: Diesel Engine Diagnostics Alt Text: A technician using professional diesel injector testing equipment to diagnose a truck engine.
How to Diagnose Fuel Injector Problems in a Diesel Engine
- Visual Inspection: Look for external fuel leaks around the injectors and fuel lines. Check the fuel filter for excessive dirt, which indicates contamination.
- Listening to the Engine: A healthy diesel has a steady rhythm. Listen for unusual clicking, knocking, or ticking sounds that could indicate a faulty injector.
- OBD-II Scan Tool: This tool reads Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from your truck's computer. Codes for misfires, fuel pressure (like P0087), or injector circuits point you toward the problem.
- Injector Balance Rate Test: This test measures how much fuel each injector delivers. A significant deviation in one injector's rate compared to others indicates a fault.
- Cylinder Contribution Test: This test assesses the power output of each cylinder. A cylinder that isn't contributing its share often has a faulty injector.
- Fuel Pressure Test: Measuring pressure and flow can reveal if the fuel pump is failing or if an injector is stuck open, causing a system-wide pressure drop.
- Compression Test: This is crucial for ruling out other issues. Low compression in a cylinder can mimic injector symptoms but may be caused by worn piston rings or valves.
For complex issues, professional diesel injector testing services offer precise diagnostics. You can also learn how to check common rail injectors for more insight.
Vehicle-Specific Issues: Volvo, Mack, and More
While the principles are similar, different manufacturers have common failure patterns. At G2 Diesel Products, our experience manufacturing injectors for Volvo, Mack, Kenworth, and Paccar gives us deep, model-specific knowledge.
| Engine Type/Manufacturer | Common Injector-Related Issue Type | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Volvo D11/D13/D16 | High-pressure fuel leaks, injector cup failures | Fuel in oil, coolant contamination, reduced power, misfires |
| Mack MP7/MP8/MP10 | Internal leakage, nozzle wear, carbon buildup | Hard starts, excessive smoke (black), decreased fuel economy |
| Paccar MX-11/MX-13 | Fuel contamination sensitivity, injector deposits | Reduced power, rough idle, DPF issues, check engine light |
| Kenworth (various) | Wiring harness issues (for electronic injectors), wear from high mileage | Intermittent misfires, erratic engine performance, DTCs |
For example, Volvo engines are known for injector cup failures that can cause fuel to leak into the oil or coolant. Mack truck injector problems often involve internal leakage and carbon buildup. Paccar engines are sensitive to fuel contamination, while some Kenworth trucks may develop wiring harness issues that mimic injector failure. Understanding these tendencies helps focus diagnostic efforts and leads to a faster, more accurate repair.
Prevention and Solutions: Keeping Your Fuel System Healthy
An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, especially for fuel injector problems diesel engines face. Proactive maintenance is the best way to extend the life of your injectors and keep your truck running reliably.

Title: Diesel Fuel Filtration Alt Text: A clean, new diesel fuel filter, a key component in preventing fuel injector problems.
Preventative Maintenance Checklist
Following these diesel fuel injector maintenance tips can prevent most common issues.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Always buy diesel from reputable, high-volume stations to avoid contaminants and ensure proper lubricity.
- Regular Fuel Filter Changes: Replace fuel filters at or before the manufacturer's recommended interval. This is your first line of defense against debris.
- Use a Quality Additive: A good diesel fuel injector cleaner with detergents helps remove carbon deposits and keeps nozzles clean for optimal combustion.
- Avoid Excessive Idling: Prolonged idling leads to lower combustion temperatures, which promotes carbon buildup on injector tips.
- Proper Fuel Storage: If you store fuel, use clean, sealed tanks protected from moisture. Water is a primary cause of injector corrosion.
- Address Warning Signs Promptly: Don't ignore symptoms like rough idling or poor fuel economy. Early diagnosis can prevent a small problem from becoming a major repair.
Repair vs. Replace: Making the Right Call
When an injector fails, you must decide whether to repair or replace it.
Repairing injectors can be economical for minor issues like clogs or some leaks. Shops can use diesel injector repair kits to clean and rebuild them. This is a viable option if the injector body is in good shape.
However, replacing injectors is often the more reliable long-term solution, especially for high-mileage or severely damaged components in modern common-rail systems. When choosing a replacement, quality is paramount. Many rebuilt or remanufactured injectors fail to meet original equipment standards. That's why selecting reputable diesel fuel injector rebuilders is critical.
The total diesel fuel injector cost includes significant labor, often 8-10 hours. Investing in quality fuel injector replacement parts that meet or exceed OEM specifications ensures reliability and prevents you from paying for the same job twice.
Frequently Asked Questions about Diesel Injector Problems
We often hear similar questions from truck owners and fleet managers dealing with the fuel injector problems diesel engines present. Here are answers to some of the most common concerns.
How often should diesel fuel injectors be replaced?
There is no single "magic number," but a general guideline is to have injectors inspected every 100,000 miles. This is not a strict replacement rule. The actual lifespan varies greatly depending on the engine model, operating conditions, fuel quality, and maintenance diligence. A proactive inspection schedule is always more cost-effective than reacting to a failure.
Can one bad injector damage an engine?
Yes, absolutely. A single faulty injector can cause severe engine damage, which is why early detection is critical. An injector stuck open can wash lubricating oil from the cylinder walls, causing accelerated wear on piston rings and liners. This excess fuel can also dilute the engine oil, leading to bearing damage. In a worst-case scenario, it can cause piston damage or catastrophic engine failure.
Can you drive with a faulty diesel injector?
While the truck might still move, it is highly not recommended. Driving with a faulty injector leads to poor performance, terrible fuel economy, and increased emissions that can damage the DPF system. More importantly, you risk causing the severe engine damage mentioned above. Your truck may also enter "limp mode," drastically reducing power to protect the engine. The safest and smartest action is to stop driving and seek professional diagnosis and repair as soon as possible.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Investment with Quality Parts and Maintenance
Dealing with fuel injector problems diesel engines present can seem daunting, but it is completely manageable with a proactive approach. Throughout this guide we’ve shown that symptoms such as rough idling, misfires, or excessive smoke almost always trace back to two root causes—fuel contamination or mechanical wear inside the injector body. By recognizing those warning signs early, you transform a potential engine-down emergency into a quick, scheduled repair.
Why Proactive Care Pays Dividends
- Fewer Road-Side Breakdowns – Planned filter changes and periodic injector balance tests cost a fraction of an unplanned tow and hotel stay for your driver.
- Better Fuel Economy – A clean, accurately metered spray pattern burns every drop, often recapturing 2–5 % in mileage within a single service interval.
- Longer Engine Life – Properly functioning injectors prevent raw fuel from washing lubricant off cylinder walls, protecting rings, liners, and bearings.
- Lower Emissions & Compliance Costs – Accurate dosing keeps soot down, lengthening DPF service life and avoiding expensive forced regens.
A 90-Day Action Plan You Can Start Today
Week 1 – Inspect for visible leaks around injector bodies and high-pressure lines. Replace any compromised seals or cracked return hoses.
Week 2 – Pull a fuel sample from the tank bottom and the primary filter bowl. Check for water, rust, or microbial “sludge.” If present, drain, polish, and treat the fuel before it reaches the rail.
Week 3 – Schedule an injector balance-rate or cylinder-contribution test during your next oil change. Flag any unit that delivers 15 % more or less fuel than its siblings.
Week 4 – Install fresh primary and secondary fuel filters, even if they are not yet at the OEM change interval. The modest cost is cheap insurance compared with an injector rebuild.
Weeks 5–12 – Log idling hours, fuel consumption, and any DTCs each week. Trends—good or bad—will be obvious in a single quarter, allowing data-driven decisions rather than guesswork.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Diesel Injection Technology
Common-rail pressures continue to climb—30,000 psi is already common in late-model heavy-duty engines, and manufacturers are testing systems above 40,000 psi to meet upcoming emissions rules. With those pressures, tolerances shrink to the sub-micron level. That means:
• Even smaller contaminants can score an injector seat. • Lubricity additives become non-negotiable. • Precise torque specs and installation cleanliness are more critical than ever.
Investing in premium filtration and high-quality replacement components today ensures you’re prepared for tomorrow’s tighter tolerances.
Partner With a Supplier That Engineers for the Long Haul
When an injector finally reaches end-of-life, the part you choose makes the difference between another 100,000 trouble-free miles and a repeat failure next quarter. At G2 Diesel Products we manufacture injectors specifically for Volvo, Mack, Kenworth, and Paccar platforms, replicating OEM flow rates and spray angles while upgrading wear surfaces where field data shows chronic failure. Every unit is bench-tested across the full duty cycle—idle, cruise, and full-load—before it ever reaches your loading dock.
Our customers report:
• Up to 50 % fewer warranty claims versus generic reman units. • Average installation-to-delivery lead times under seven days, minimizing fleet downtime. • Technical phone support from career diesel engineers, not call-center scripts.
Final Takeaway
Your truck’s profitability rides on a razor-thin margin of fuel control delivered by a component smaller than a spark plug. Treat that injector system with the same respect you give the engine block itself: clean fuel, on-time maintenance, and—when the day finally comes—replacement parts built to out-perform the originals. Do that, and you’ll keep more trucks on the road, more loads delivered on time, and more revenue on your bottom line.
Ready to protect your investment with parts you can trust? Explore our robust and reliable Volvo, Mack, Kenworth, and Paccar diesel fuel injectors today, and let G2 Diesel Products keep your fleet running at peak efficiency.
